
CBD: How It Works and Top Health Benefits
March 15, 2022
In This Healthy Insight:
What is the endogenous cannabinoid system?
The nervous system is comprised of specialized cells and nerves that transmit signals throughout the body acting as a communication highway to keep our bodies in check.
Much like the nervous system, the endogenous cannabinoid system (ECS) is a self-regulating system comprised of cell receptors and corresponding molecules throughout the body that work to maintain homeostasis and optimal health. However, unlike the nervous system the ECS works in reverse – sending signals backwards in response to changing circumstances. There are three components involved in the endocannabinoid system – cannabinoids, receptors and enzymes.
What are cannabinoids?
Endogenous cannabinoids are made naturally inside the body and found in our brain, organs, tissues, glands and immune cells to help regulate numerous physiological functions:
- Appetite
- Brain development
- Coordination
- Emotional responses
- Inflammation
- Memory
- Mood
- Pain perception
- Sleep
Exogenous cannabinoids, on the other hand, come from outside the body. These interact with the ECS and mimic the effects of our natural cannabinoids.
What are cannabinoid receptors?
There are two types of cannabinoid receptors naturally found on the surface of cells all over the body. Cannabinoid 1 receptors (CB1) exist throughout the body but are most abundant in the brain and spinal cord, specifically the areas associated with the functions they benefit. For example, the hypothalamus to help regulate appetite and the amygdala to help regulate emotional processing. CB2 receptors are found in the peripheral nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, spleen, tonsils, thymus gland, on immune cells and even skin cells.
Cannabinoid receptors and their corresponding chemicals act like a lock and key. When cannabinoids interact with their receptors it starts a feedback loop to regulate different physiological processes including sleep, appetite, memory, temperature, emotional responses, perception of pain and inflammation. How do they do this? They use retrograde signaling to convey messages to modulate nervous system activity to maintain balance and optimal functioning.
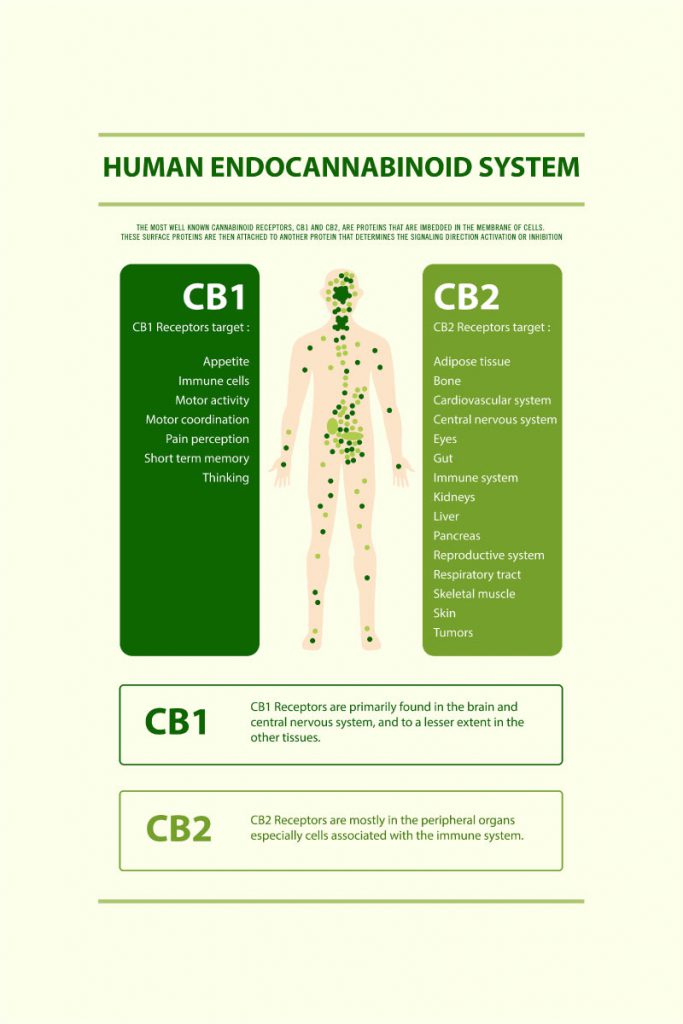
What are the role of enzymes?
There are two enzymes are responsible for making, regulating and degrading the amount of endocannabinoids – fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL). The system works best when endocannabinoids, enzymes and receptors are all present and interact correctly.
When there aren’t enough endocannabinoids, functionality suffers. So, how do we ensure that our bodies have all the necessities for optimal performance?
- Diet. Eat foods that are rich in polyphenols and omega-3 fatty acids such as nutmeg, turmeric, walnuts, certain types of seafood and spinach.
- Exercise. Exercise allows the release of neurotransmitters and endocannabinoids necessary to keep the body in balance.
- Supplementing. Exogenous cannabinoids bind to the appropriate receptors to modulate and enhance the endocannabinoid system.

Cannabidiol (CBD) + Benefits
Since we have an endocannabinoid system, our bodies are designed to use CBD. If you have ever experienced a runner’s high, then you’ve experienced the send of well-being that your natural cannabinoids have created.
There are two types of CBD products – hemp-based and marijuana-based – the difference is the THC content. Hemp-based CBD is legal in all 50 states and has negligible amounts of THC, meaning that it is non-psychoactive and you can find it in different retailers or health food stores. Marijuana-based CBD contains greater amounts of THC and is allowed in certain states through local dispensaries. Recent research has recognized CBD as an alternative for variety of everyday issues.
Pain
CBD alters or inhibits neuronal signals that are sent from the affected area to the brain so that our perception of pain is altered, providing relief and comfort.
Inflammation
CBD indirectly activates immune cells that release anti-inflammatory mediators and reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines. Since both receptors are found on cells in joint cartilage, muscles and certain bones, many people find relief from the daily wear and tear on these areas. CBD also blocks enzymes that target and degrade bone-building compounds and therefore, aid in bone cell formation.
Stress, Sleep, Mood and Mental Health
The main focus of the ECS is to restore balance and homeostasis to our bodies. Many people who struggle with stress management, sleep, mood and mental health may have an imbalance in their brain chemicals. CBD acts on the receptors in our brain to boost signaling and restore balance fostering better sleep and manageable levels of stress hormones.
Overall Protection
CB2 receptors are abundant in skin cells. CBD topicals provide antioxidant protection to fight free radicals from damaging environmental occurrences such as UV rays or pollutants. Since it decreases damage, CBD can promote healing and improve skin health, including acne.
Activated CB2 receptors send messages to macrophages to destroy beta-amyloid protein, the main component of plaque in brain, to keep the memory sharp.
CBD is also known to be neuroprotective because it decreases toxicity in neurons, has antioxidant protection for these neurons and promotes the synthesis of new neurons.
How to use CBD?
CBD Oil is most often ingested in softgels or capsules, but is also available in balms, drops, sprays and more. Always purchase a high-quality oil without chemical additives from a reputable, well-established company. Since CBD Oil is relatively new on the market and exact dosing isn’t well-established, start with the recommended dosage on the package. Some may notice an immediate change while others may not notice anything for multiple weeks.
If you’re looking for some high-quality CBD products, shop here.



